
The Overview dashboard lets you monitor important SQL performance, replication, and storage metrics. To view this dashboard, access the DB Console and click Metrics on the left-hand navigation bar. The Overview dashboard is displayed by default.
Dashboard navigation
Use the Graph menu to display metrics for your entire cluster or for a specific node.
To the right of the Graph and Dashboard menus, a range selector allows you to filter the view for a predefined timeframe or custom date/time range. Use the navigation buttons to move to the previous, next, or current timeframe. Note that the active timeframe is reflected in the URL and can be easily shared.
All timestamps in the DB Console are shown in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
The Overview dashboard displays the following time series graphs:
SQL Statements
In the node view, the graph shows the 10-second average of the number of
SELECT/INSERT/UPDATE/DELETEqueries per second issued by SQL clients on the node.In the cluster view, the graph shows the sum of the per-node averages, that is, an aggregate estimation of the current query load over the cluster, assuming the last 10 seconds of activity per node are representative of this load.
See the Statements page for more details on the cluster's SQL statements.
Service Latency: SQL, 99th percentile
Service latency is calculated as the time in nanoseconds between when the cluster receives a query and finishes executing the query. This time does not include returning results to the client.
In the node view, the graph shows the 99th percentile of service latency for the node. Over the last minute this node executed 99% of queries within this time, not including network latency between the node and the client.
In the cluster view, the graph shows the 99th percentile of service latency across all nodes in the cluster. There are lines for each node in the cluster. Over the last minute the node executed 99% of queries within this time, not including network latency between the node and the client.
Replicas per Node
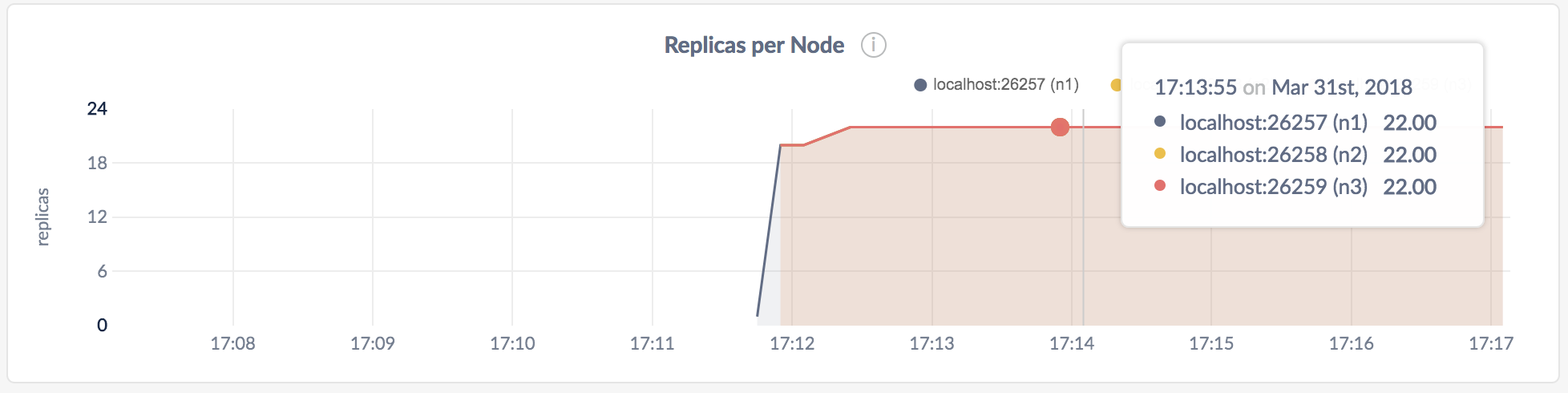
Ranges are subsets of your data, which are replicated to ensure survivability. Ranges are replicated to a configurable number of CockroachDB nodes.
In the node view, the graph shows the number of range replicas on the selected node.
In the cluster view, the graph shows the number of range replicas on each node in the cluster.
For details about how to control the number and location of replicas, see Configure Replication Zones.
The timeseries data used to power the graphs in the DB Console is stored within the cluster and accumulates for 30 days before it starts getting truncated. As a result, for the first 30 days or so of a cluster's life, you will see a steady increase in disk usage and the number of ranges even if you aren't writing data to the cluster yourself. For more details, see this FAQ.
Capacity
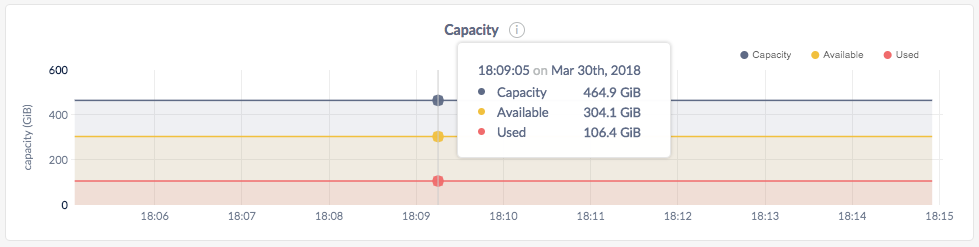
You can monitor the Capacity graph to determine when additional storage is needed (e.g., by scaling your cluster).
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Capacity | The maximum store size. This value may be set per node using --store. If a store size has not been set, this metric displays the actual disk capacity. See Capacity metrics. |
| Available | The free disk space available to CockroachDB data. |
| Used | The disk space in use by CockroachDB data. This excludes the Cockroach binary, operating system, and other system files. |
Capacity metrics
The Capacity graph displays disk usage by CockroachDB data in relation to the maximum store size, which is determined as follows:
- If a store size was specified using the
--storeflag when starting nodes, this value is used as the limit for CockroachDB data. - If no store size has been explicitly set, the actual disk capacity is used as the limit for CockroachDB data.
The available capacity thus equals the amount of empty disk space, up to the value of the maximum store size. The used capacity refers only to disk space occupied by CockroachDB data, which resides in the store directory on each node.
The disk usage of the Cockroach binary, operating system, and other system files is not shown on the Capacity graph.
If you are testing your deployment locally with multiple CockroachDB nodes running on a single machine (this is not recommended in production), you must explicitly set the store size per node in order to display the correct capacity. Otherwise, the machine's actual disk capacity will be counted as a separate store for each node, thus inflating the computed capacity.
Summary and events
Summary panel
A Summary panel of key metrics is displayed to the right of the timeseries graphs.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Total Nodes | The total number of nodes in the cluster. Decommissioned nodes are not included in this count. |
| Capacity Used | The storage capacity used as a percentage of usable capacity allocated across all nodes. |
| Unavailable Ranges | The number of unavailable ranges in the cluster. A non-zero number indicates an unstable cluster. |
| Queries per second | The total number of SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE queries executed per second across the cluster. |
| P99 Latency | The 99th percentile of service latency. |
If you are testing your deployment locally with multiple CockroachDB nodes running on a single machine (this is not recommended in production), you must explicitly set the store size per node in order to display the correct capacity. Otherwise, the machine's actual disk capacity will be counted as a separate store for each node, thus inflating the computed capacity.
Events panel
Underneath the Summary panel, the Events panel lists the 5 most recent events logged for all nodes across the cluster. To list all events, click View all events.
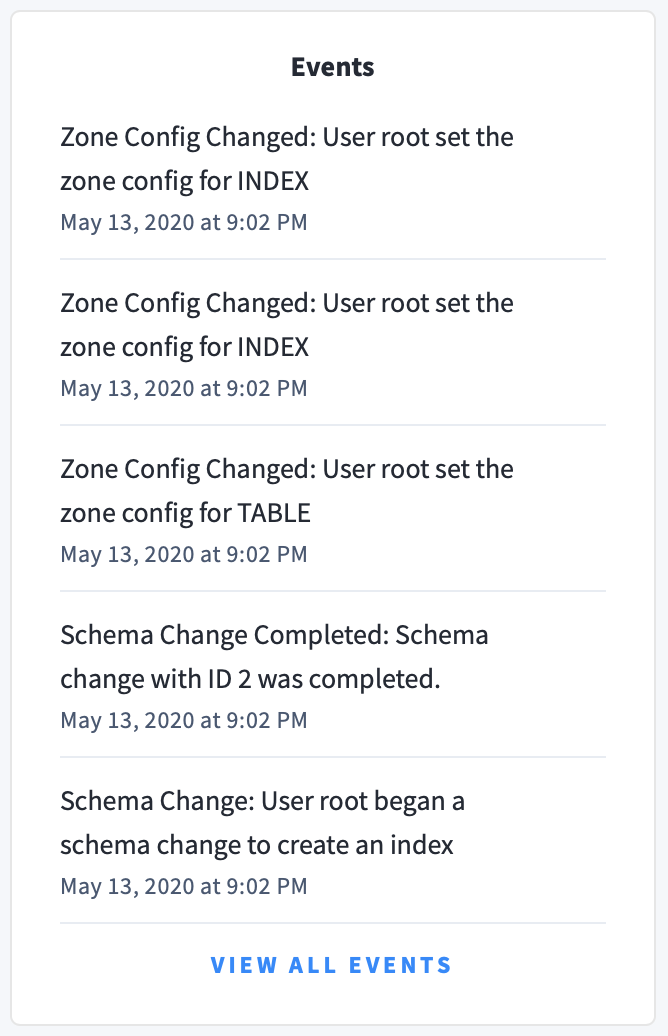
The following types of events are listed:
- Database created
- Database dropped
- Table created
- Table dropped
- Table altered
- Index created
- Index dropped
- View created
- View dropped
- Schema change reversed
- Schema change finished
- Node joined
- Node decommissioned
- Node restarted
- Cluster setting changed